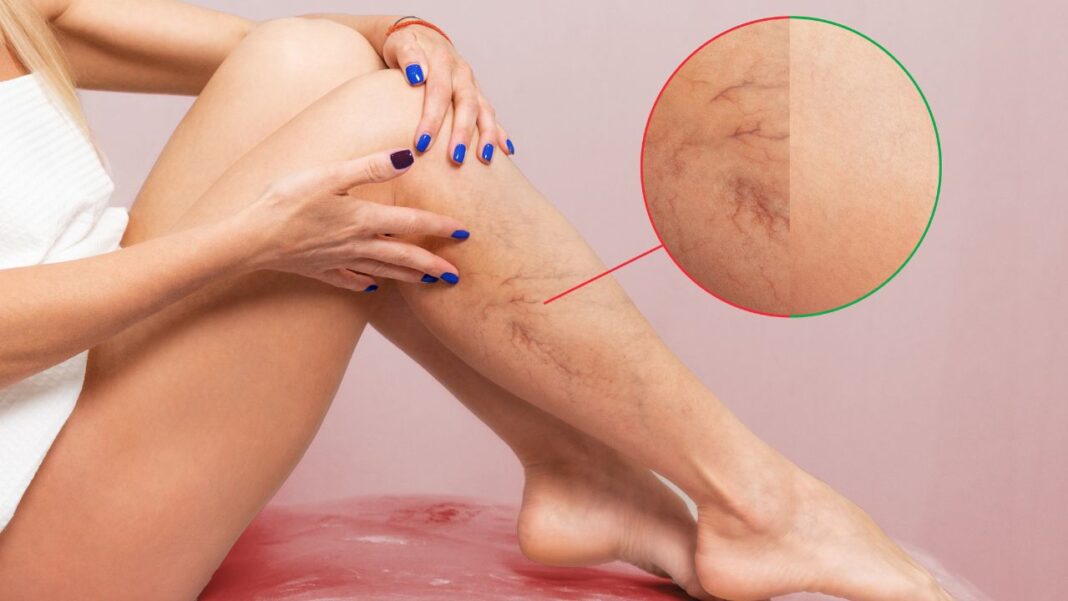
Varicose veins are a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often causing discomfort and aesthetic concerns.
These enlarged and twisted veins, typically found in the legs, can be both a cosmetic issue and a medical one.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, and preventive measures related to varicose veins can empower those affected to seek appropriate interventions and make informed choices about their health.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
The symptoms of varicose veins can range from mild to severe and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
The most recognisable symptom is the appearance of bulging, dark purple or blue veins just beneath the skin.
The following are additional symptoms that may accompany varicose veins, including:
Aching or heavy legs: Many individuals experience leg heaviness or fatigue, particularly after prolonged standing or sitting.
Swelling: Swollen legs or ankles may occur, especially by the end of the day or after prolonged standing.
Pain or discomfort: Some people report dull aches, throbbing, or a burning sensation in the affected areas.
Cramping: Nighttime leg cramps may also occur, adding to the discomfort.
Skin changes: Over time, the skin may become discolored, and in severe cases, ulcers or sores may develop.
Recognising these symptoms early is crucial for effective management and treatment of varicose veins.
Causes and Risk Factors
Varicose veins develop when the one-way valves within the veins weaken or fail. This prevents blood from flowing efficiently back to the heart. Instead, blood pools in the veins, causing them to become enlarged and twisted.
Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition:
Age: As individuals age, their veins can lose elasticity, making them more prone to stretching and causing valve failure.
Genetics: A family history of varicose veins significantly increases the risk of varicose veins. There is a possibility of developing or increasing if parents or siblings have the condition.
Gender: Women are more likely than men to experience varicose veins, partly due to hormonal factors. The factors that contribute to vein problems amongst women are Pregnancy, menopause, and the use of hormone replacement therapy, etc.
Obesity: Carrying excess weight adds pressure to the veins, which can lead to valve failure over time.
Lengthy standing or sitting: Jobs or lifestyle choices that involve extended periods of standing or sitting can increase the risk. This is particularly relevant for those in professions such as retail, teaching, or office work.
Complications of Varicose Veins
While many cases of varicose veins are relatively harmless, serious complications can arise if the condition is left untreated.
Some potential complications include:
Blood clots: Blood clots can form in varicose veins, leading to pain, swelling, and potentially serious conditions like thrombophlebitis.
Ulcers: Ulcers may develop near the ankle, characterized by open sores due to prolonged pressure and poor circulation.
Skin changes: The skin around varicose veins can become discolored, hardened, and may even appear shiny due to underlying changes in circulation.
Bleeding: In severe cases, varicose veins may bleed if injured, posing a significant health risk.
Seeking medical advice at the first sign of varicose veins can help mitigate these potential complications and ensure timely intervention.
Preventive Measures
Preventing varicose veins or minimising their progression is possible by following several lifestyle changes and interventions. Prevention is better than a cure. It is essential to adopt a proactive approach, particularly for individuals with known risk factors.
Here are some effective preventive methods:
1. Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity promotes circulation. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling improve blood flow and can help strengthen the leg muscles, providing better support for the veins.
2. Maintain a healthy weight: Keeping your weight within a healthy range reduces the pressure on the veins, decreasing the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
3. Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity: If your job involves sitting or standing for long hours, take frequent breaks to move around. Elevating your legs periodically helps reduce venous pressure.
4. Wear compression stockings: Compression stockings provide gentle pressure to the legs, promoting better blood flow and reducing the chances of varicose vein progression.
5. Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain overall vascular health and can improve circulation.
6. Dietary choices: A balanced diet rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats can help maintain vein health. Foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains support overall vascular function.
In conclusion, awareness surrounding varicose veins is essential for effective management and prevention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors can help individuals recognise their condition early and seek appropriate medical advice.
Proactive lifestyle choices can significantly lower the risk of developing varicose veins and improve overall leg health.
If you experience symptoms or have concerns about varicose veins, consult with a healthcare professional for guidance tailored to your specific situation. Making informed choices today can lead to healthier, more comfortable tomorrows.